How does Google search work?
Google search is our door to the Internet. And it’s likely the door to your website too.
In this article, no technical SEO vocabulary, just plain text, and illustrations to help you understand how Google search works.
On a high level, search engines are simple. I won’t get into details or list the exact factors Google uses to rank your website (because nobody knows).
At the end of the article, you will understand how Google works and why you need to optimize your website for search engines. Plus, I will give you some tools and a high-level approach to optimize your site.
Let’s start!
Google is a search engine that connects people publishing content on websites (let’s call them “website owners”) and people consuming the content (they will be called “users”).
To understand Google search, we need to cover the relationship between:
1) Google and website owners
2) Google and users
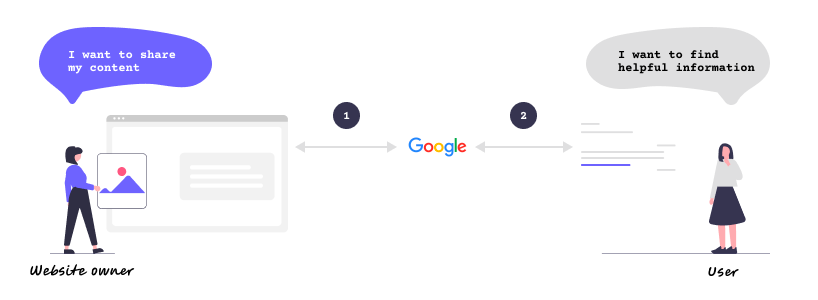
First, let’s understand the relationship between Google and website owners.
1) Organizing information from the web.
In this phase, the action is between Google and the website owner.
Website owners create content and want to reach their audience. To gain traffic and visibility, they make their website available on Google.
But, how will Google do this?
Google must understand and sort the website and do it in 2-steps:
- Crawling website: Google sends robots online to analyze the website and identify all the relevant information. You might have heard them through a file called robot.txt on your website.
crawling illustration
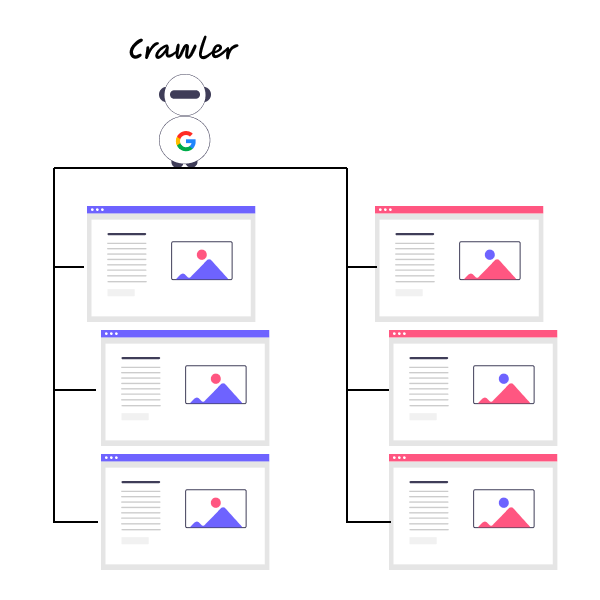
2. Indexing information: Google takes notes of the information on the website and indexes it in its Gigantic database.
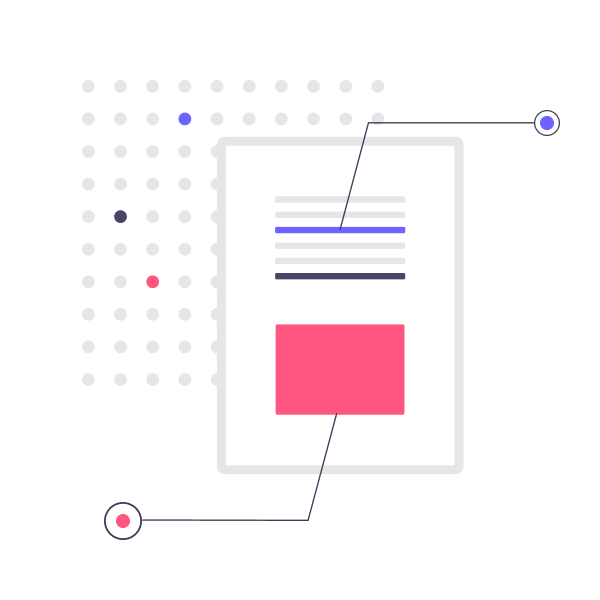
Another way to see it is to imagine a library on new-books-delivery day. To make books accessible, the librarian must first review the book to understand its content (crawling). Once they know the topic and author, the librarian will store it on the relevant shelf(indexing).
Today, your website is automatically crawled and indexed. As a website owner, ensure your website is indexed by typing: site:[yourwebsite. com] on Google.
If it’s not indexed, this article covers it in detail: https://ahrefs.com/blog/google-index/
Now that your website is on Google, let’s focus on the relationship between Google and users.
2) Generating relevant results for users
Now, imagine users looking for the correct information on the internet. Where will they find this, on which website?
When people don’t know something, they can simply type the first keywords that come to mind into their search bar and then press enter.
In a split second, the most relevant websites based on your searched keywords appear instantly.
To perform this wonder, the Google search team decided on a 4-step process to sort and rank the billions of websites and show you a handful of relevant ones:
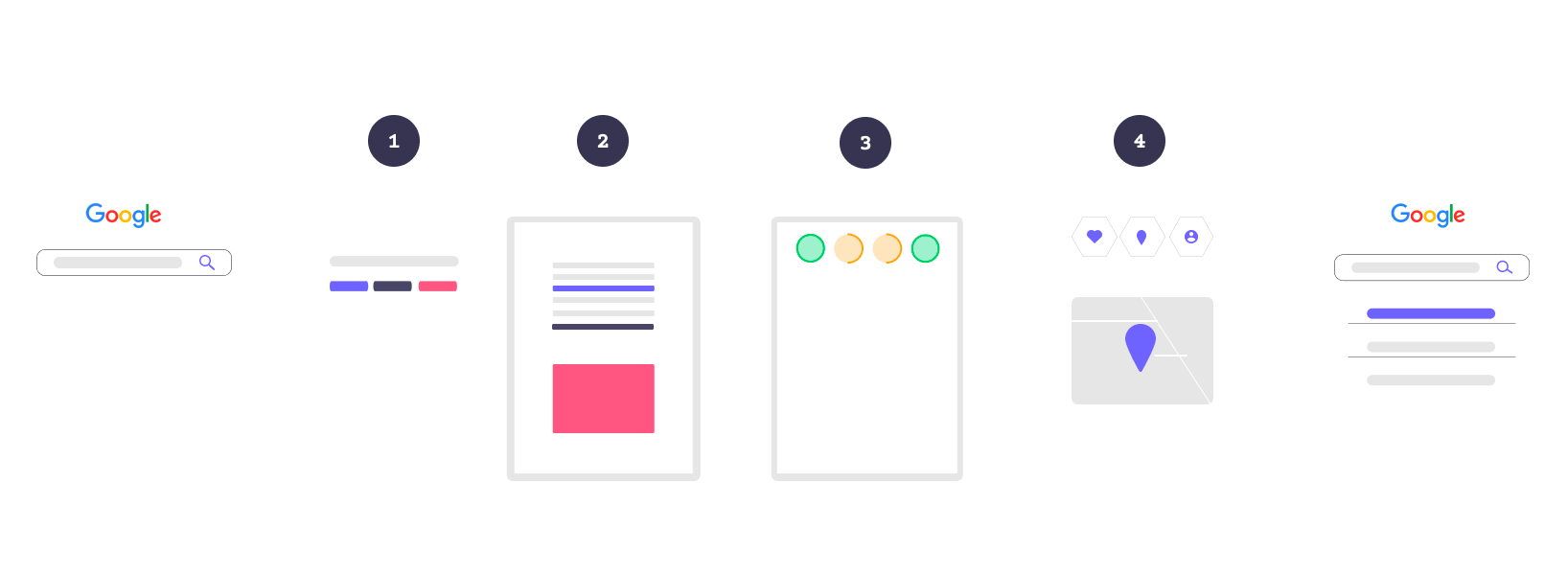
A) Relevance of your content:
First, Google searches for web pages indexed in its database, including the same keywords. Yes, we are talking about millions of results. This is the number you see on Google search.
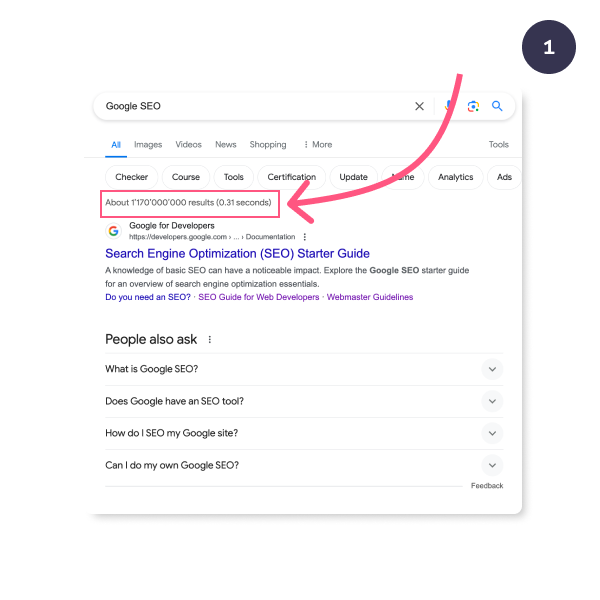
Millions (or 1.17 billion in our example above) of links are not helpful. Google needs to rank and show the most helpful one first.
B) Quality of your content
Content quality is an abstract concept, but Google has a 2 criteria solution:
1) How relevant is your content?
Google considers the number and quality of backlinks (website linking to your website) a strong indicator of content quality. More backlinks generally indicate higher-quality content.
2) How valuable is your content for your users?
Next, Google assesses the usefulness of your content. They look for signals demonstrating expertise, experience, authority, and trust about a topic (E-E-A-T). Simply put, Google judges the quality of your website based on the credibility of the page, the author, and the website's safety.

How do they do this? How is it possible to know what is useful?
Google pays people to navigate websites and rate them based on quality. Then, Google feeds its machine learning algorithm to assess other websites at scale. If you're curious to know more, have fun reviewing the 170 pages of Google quality guidelines for reviewers 😅.
It’s not yet a perfect solution; I recently shared a story of hackers mocking Google on their quality assessment.
3. Usability of webpages
After a quality review, if some websites perform the same, Google will favor the best page experience. In other words, Google will look at the Lighthouse score to determine whether performance, SEO, accessibility, and best practices are respected.

The higher your score, the better ranking you get.
4. Content and setting
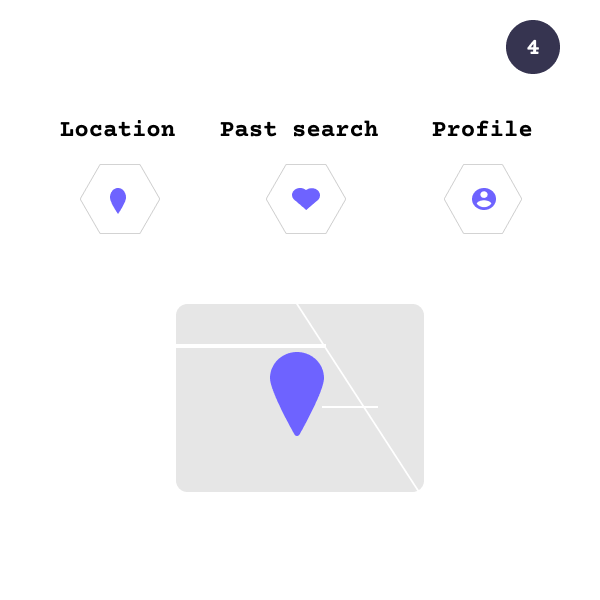
Last, information such as location, past search history, and search settings helps Google ensure that the results are relevant to you at the moment.
Our users will receive information based on their location, search history, and profile.
Ranking the search results
Google goes through all the above steps in less than 0.3 seconds and provides a ranking of the most helpful links. Most of us do not scroll further than the first 10 links and do not click on more than 3 websites.
If you want to learn more about search engines, visit Google’s dedicated website
https://guidelines.raterhub.com/searchqualityevaluatorguidelines.pdf
Conclusions:
Understanding how search works is a crucial step to creating better websites.
What should website owners and webmasters do to optimize their websites for search engines?
- Increase the relevance of your content: Match your users’ relevant keywords with your website content.
Without these, your website won’t be considered by Google to show. - Improve the quality of your content and website: Create helpful content people will love to share.
If nobody links to your website, Google will assume it’s poor quality, even if you created the best content… - Build a frictionless website: Focus on performance, usability, best practices, and website accessibility.
If you read an article, watch a video, or receive advice that does not fall into those three main categories, please consider ignoring it. People will always add confusion, distraction, and technicalities to sell you a service you don’t need.
In my next article, I will cover the basic recommendations to make your website relevant for Google. The advice will help you increase the on-page experience and the relevance of your website.
